Federating the Social Web
Prospectus Presentation
Community Data Science Collective
Northwestern University
Background
The social web’s “wicked problems”—those with many stakeholders and impossible to solve without tradeoffs:
Content moderation1
Discovery2
Norms (Establishing and Maintaining)



Challenges in the Current Social Web Ecosystem
Many social web services have produced controversy because they (and their communities) have gatekeeping powers.1
Their operation and development follow the needs of their stakeholders.2
While some of these websites use volunteers, there is still a top-down structure to their operation (e.g. Reddit mods vs. admins).3
Alternatives exist, but networks effects help entrench incumbents.4
Moody v. NetChoice 
European Union Digital Services Act 
Protocols vs. Platforms
Rather than building new protocols, the internet has grown up around controlled platforms that are privately owned. These can function in ways that appear similar to the earlier protocols, but they are controlled by a single entity1
| PROTOCOLS | PLATFORMS |
|---|---|
| Decentralized: Power distributed across many independent implementations | Centralized: Power concentrated within single corporate entities |
| Open: Interoperable standards allowing anyone to build compatible services | Closed: Walled gardens with controlled access and developer limitations |
| User-Controlled: Users choose preferred clients and implementations | Company-Controlled: Company dictates features, rules, and content policies |
| Example: Email (SMTP, IMAP, POP3) | Example: Facebook |
The Early Social Web Pre-dated Platforms
Early social online communities such as bulletin board systems (BBS) and USENET were independently operated.1



Image via Kes47 (CC BY-SA). See Baran1.
The Fediverse
A collection of social servers
Interoperability via (mainly) ActivityPub protocol
Software like Mastodon and Pleroma
Why Study The Fediverse?
The Fediverse faces similar problems to other organizations on the social web, but have different motivations and stakeholders.
Studies
The effects of de-federation (inter-server sanctions)1
Server recommendation system (newcomers and server choice)2
Moderating the Fediverse (rules and enforcement)
Remaining Work
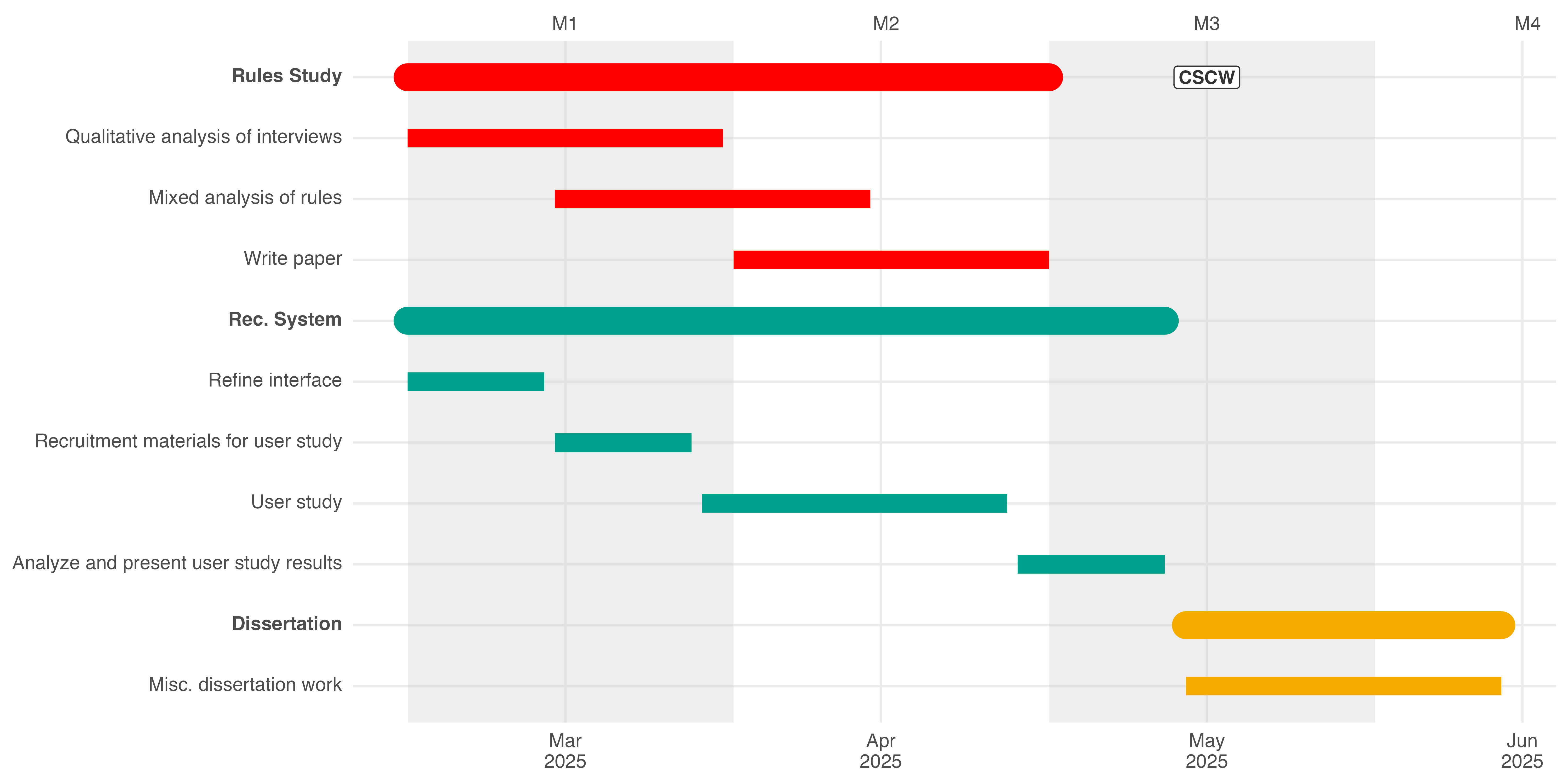
Figure 1: Gantt chart for the timeline and major milestones remaining.
The Effects of Group Sanctions on Activity and Toxicity
Colglazier, Carl, Nathan TeBlunthuis, and Aaron Shaw. “The Effects of Group Sanctions on Participation and Toxicity: Quasi-experimental Evidence from the Fediverse.” In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, vol. 18, pp. 315-328. 2024.
Fediverse servers are decentralized and autonomous.
This means while they have almost complete control over their own servers, they cannot control what happens on other servers.
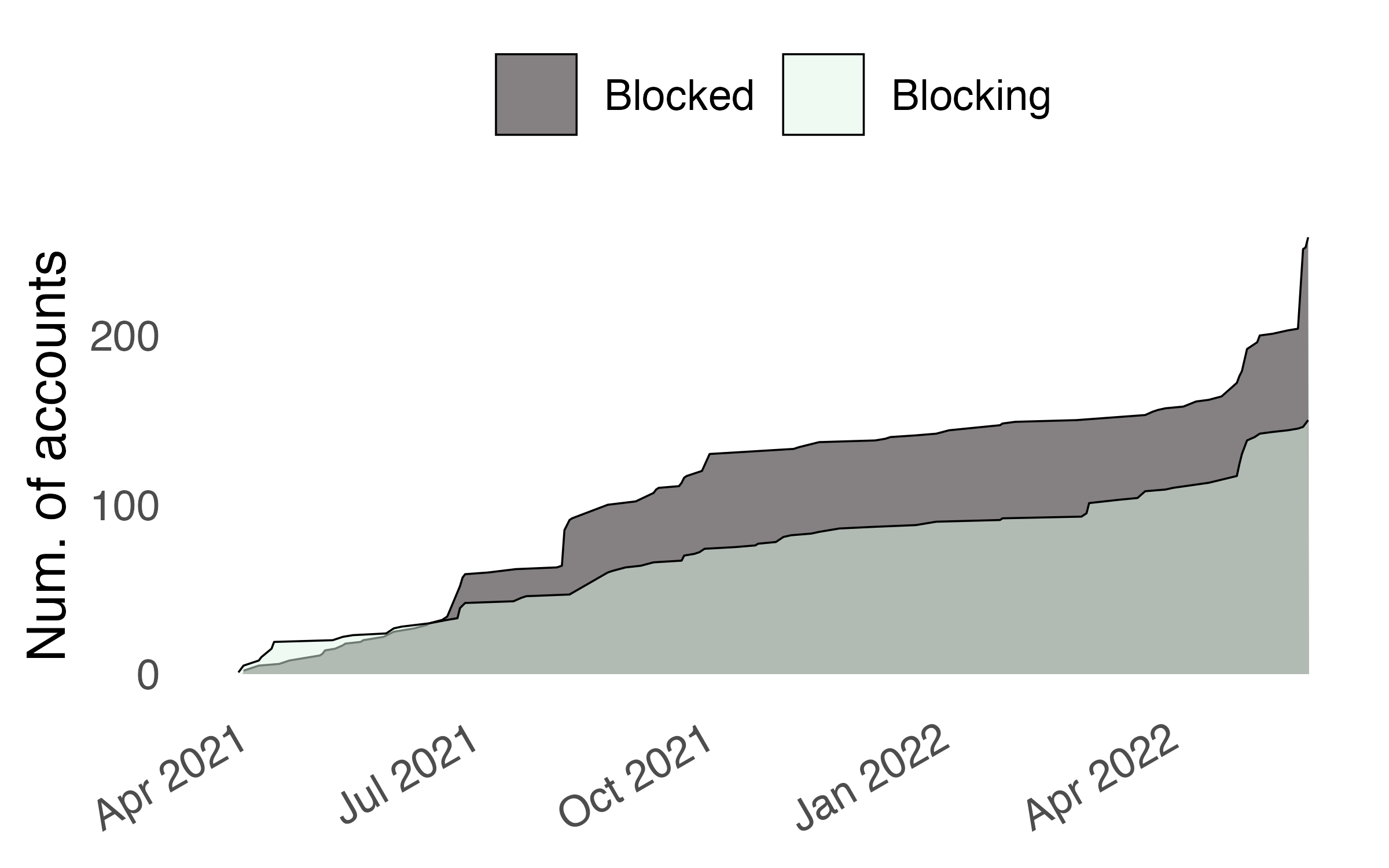
Servers may decide another server is more trouble than they are worth and block the server—an action called de-federation.
For the accounts who lose connections, what are the effects on activity and toxicity?
Data

We gathered de-federation events where accounts who previously interacted no longer could due to a new block. We then matched these accounts with synthetic controls.
De-federation reduced activity on blocked servers, but not on blocking servers
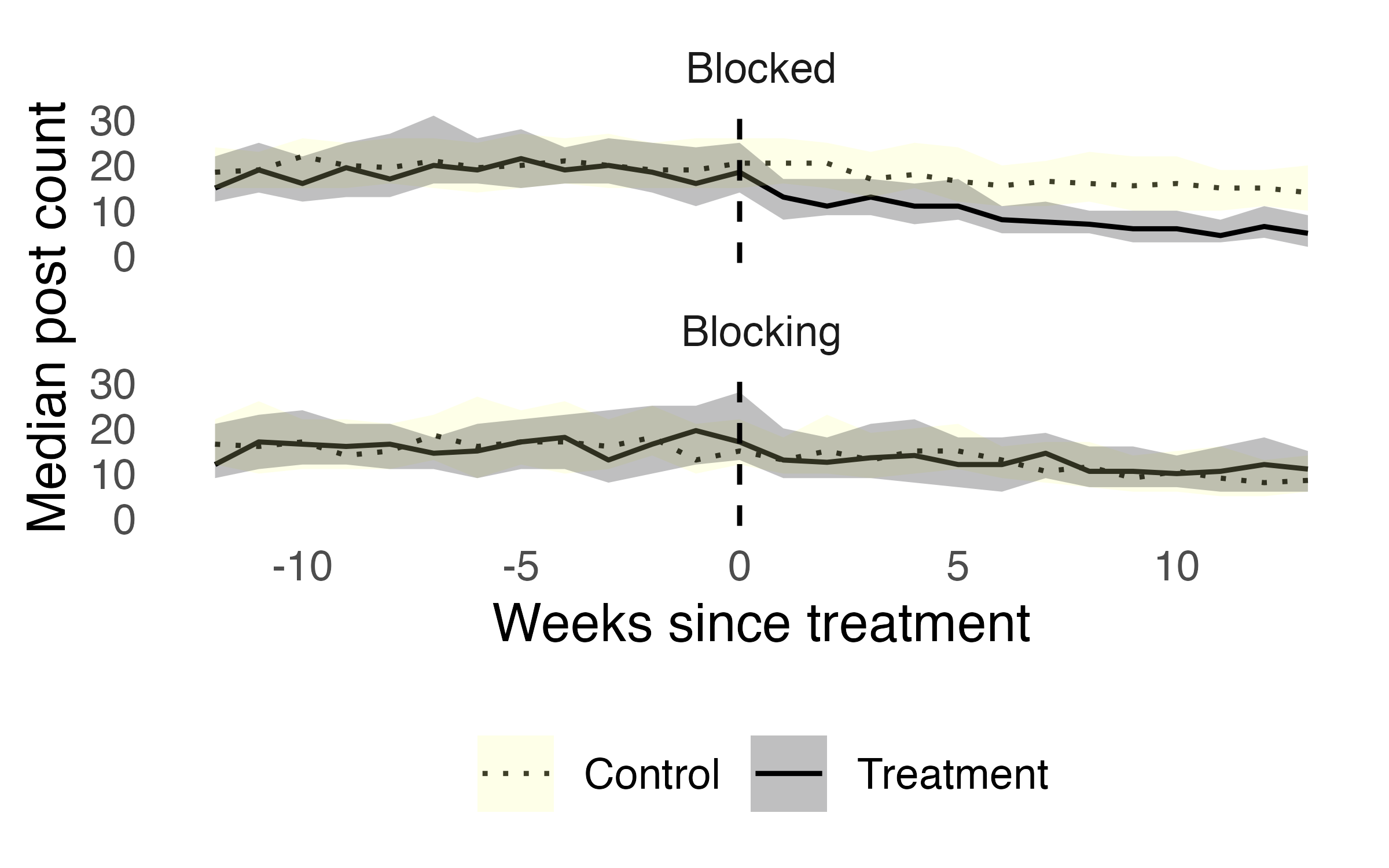
| Group | median | W | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| \(U_0\) | -135.5 | 41197.5 | 0.000 |
| \(C_0\) | -18.0 | 35762.0 | 0.143 |
| \(U_1\) | -54.5 | 12413.0 | 0.122 |
| \(C_1\) | -53.5 | 12520.0 | 0.091 |
| \(\Delta_0\) | -39.0 | 39927.0 | 0.000 |
| \(\Delta_1\) | 3.0 | 10645.5 | 0.421 |
We found no change in toxicity
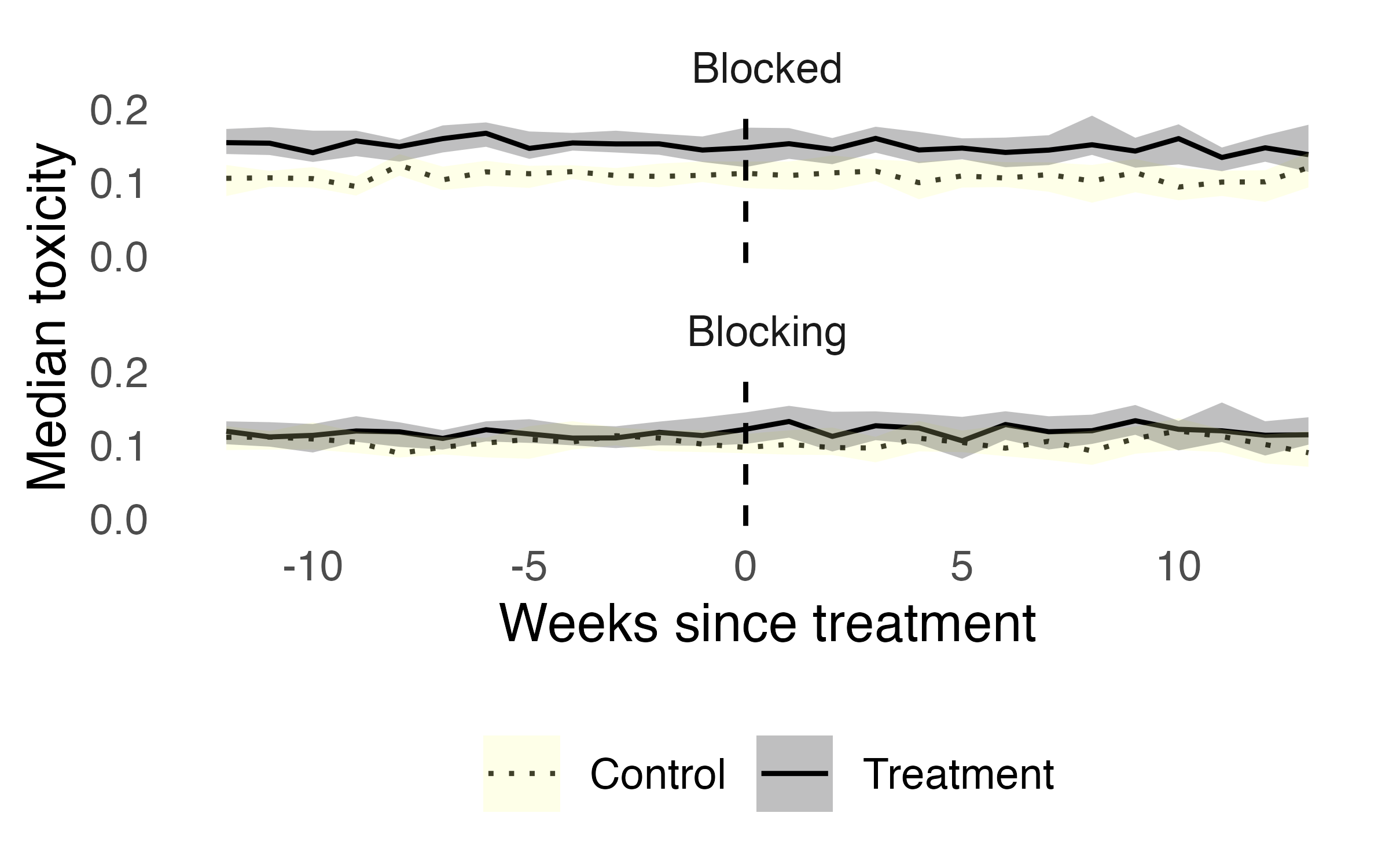
| Group | median | W | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| \(U_0\) | -0.006 | 17746 | 0.538 |
| \(C_0\) | 0.004 | 14000 | 0.950 |
| \(U_1\) | -0.008 | 6514 | 0.619 |
| \(C_1\) | 0.001 | 5546 | 0.873 |
| \(\Delta_0\) | -0.005 | 17161 | 0.072 |
| \(\Delta_1\) | 0.000 | 6414 | 0.305 |
Takeaways
Previous research into group sanctions show they can be effective in altering anti-social behavior,1 but communities do not exist in isolation and users can continue their operations off-platform.2
We find:
De-federation can be effective at reducing activity for users on blocked servers
No evidence of blowback on toxicity for any affected users
Any decentralized online social network will have de-federation or a similar mechanism.
Server Recommendations
Colglazier, Carl. “Do Servers Matter on Mastodon? Data-driven Design for Decentralized Social Media.” In 1st International Workshop on Decentralizing the Web (2024).
Millions of newcomers joined Mastodon after Elon Musk bought Twitter
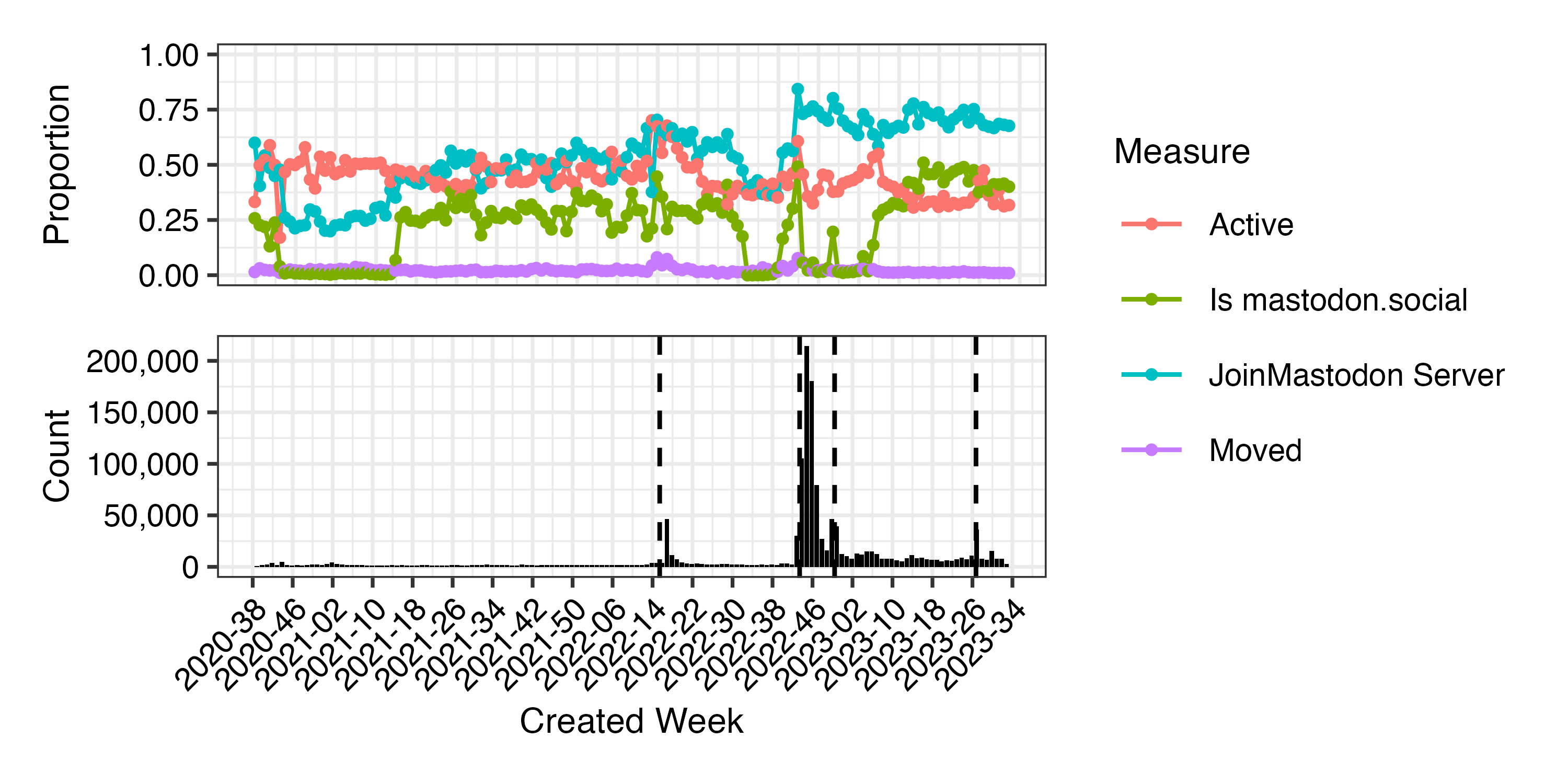
Figure 5: Accounts in the dataset created between January 2022 and March 2023.
Many people find the Mastodon onborading process confusing
Onboarding newcomers is essential for online communities.1
Compared to commercial social media, Mastodon onboarding is harder because newcomers need to pick a server.
Do some Mastodon servers retain newcomers better than others?
Smaller, less general servers are more likely to retain new accounts
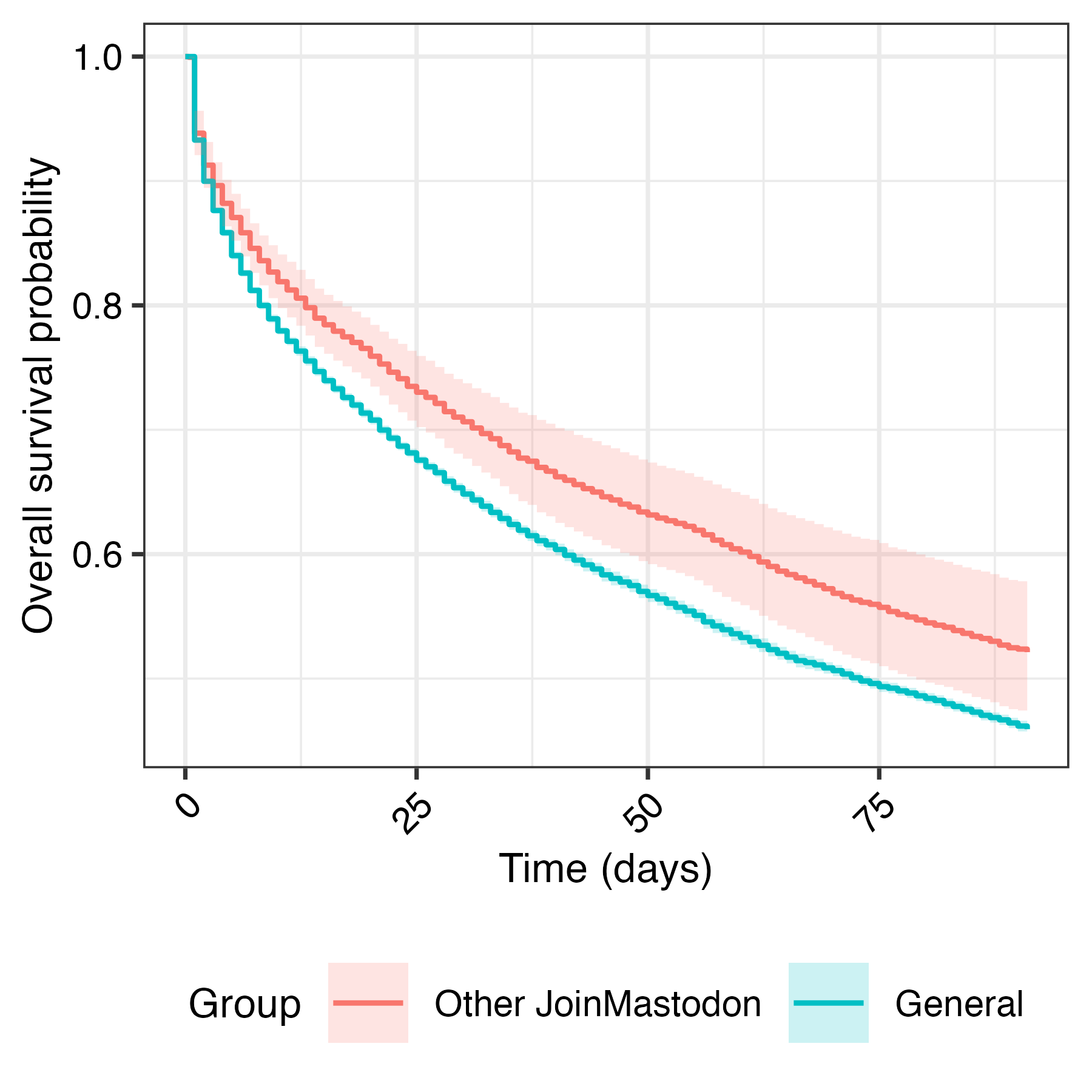
| Term | Estimate | Low | High | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Join Mastodon | 0.115 | 0.972 | 1.296 | 0.117 |
| General Servers | 0.385 | 1.071 | 2.015 | 0.017 |
| Small Server | -0.245 | 0.664 | 0.922 | 0.003 |
Accounts that move between servers are more likely to move to smaller servers
| Model A | Model B | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coef. | Std.Error | Coef. | Std.Error | |
| (Sum) | -9.529 | ***0.188 | -10.268 | ***0.718 |
| nonzero | -3.577 | ***0.083 | -2.861 | ***0.254 |
| Smaller server | 0.709 | ***0.032 | 0.629 | ***0.082 |
| Server size (outgoing) | 0.686 | ***0.013 | 0.655 | ***0.042 |
| Open registrations (incoming) | 0.168 | ***0.046 | -0.250 | 0.186 |
| Languages match | 0.044 | 0.065 | 0.589 | 0.392 |
Our analysis suggests…
- Accounts on large, general servers fare worse
- Moved accounts go to smaller servers
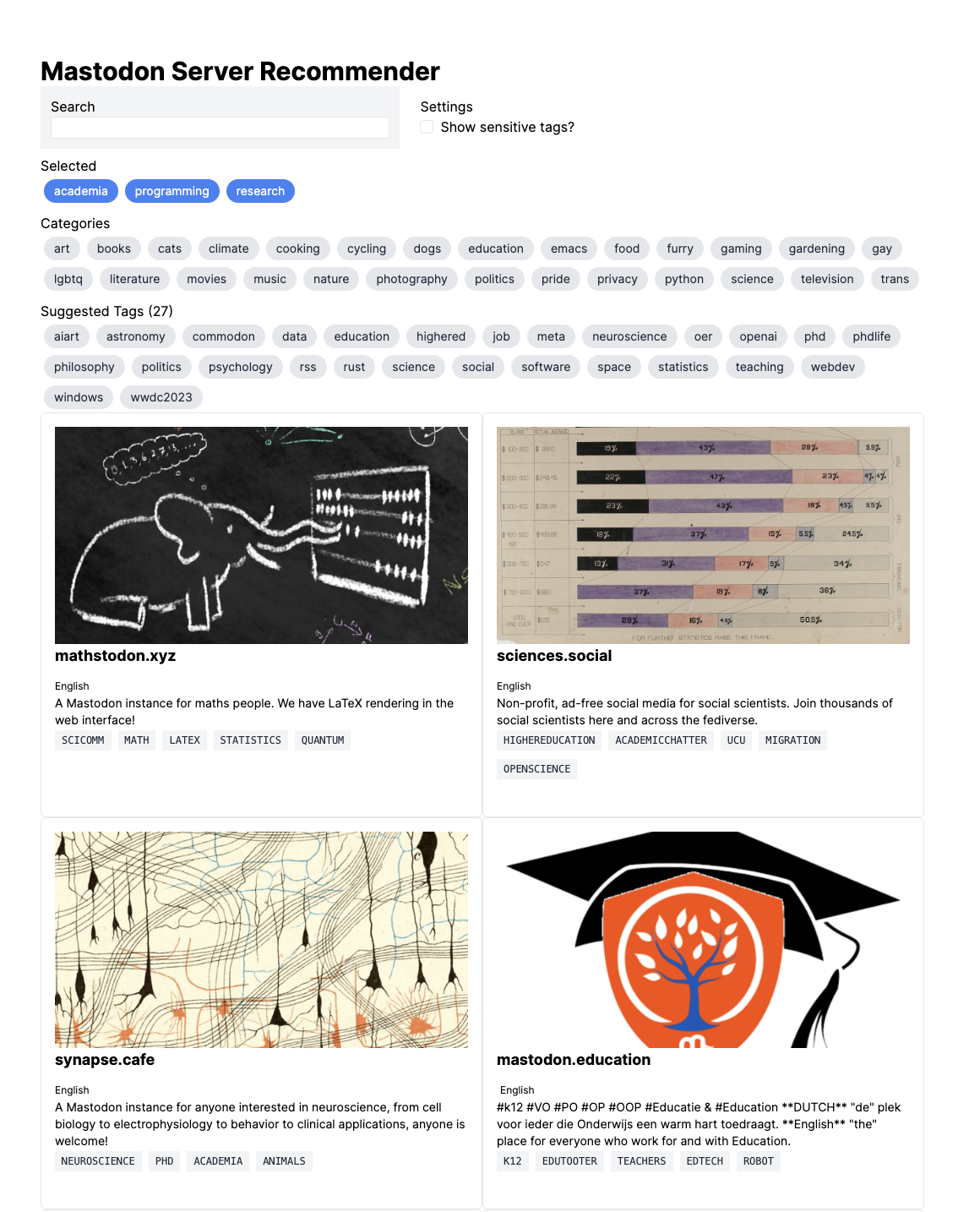
Can we build a system that helps people find servers?
Constraints
Consent: servers should be able to choose whether to participate
Privacy: do not reveal information about individual accounts
Decentralization: do not concentrate data in one place
Openness: use shared standards and protocols
Concept
A decentralized, tag-based collaborative filtering system
Each server reports their top tags from the last three months
Learn from these reports and from other servers which tags are most important for each server
Recommend servers based on selected tags of interest
Implementation
Report top hashtags used by the most accounts on each server
For robustness, drop hashtags used by too few accounts or servers
Build an \(m \times n\) server-tag matrix \(M\)
Normalize with Okai BM25 TF-IDF and L2 normalization1
Apply singular value decomposition (SVD) on \(M\) to create a new matrix \(M'\)
Match servers to selected tags using cosine similarity
SVD illustration via CMG Lee CC BY-SA 4.0
Demo
https://carlcolglazier.com/demos/deweb2024/
Evaluation
Recommendation systems attempt to be predictive.
What are we trying to predict? Out-of-sample data:
Train/test split
Posts just before our three month period
Accounts that move servers
User study
We want to also get information from potential real-world users.
To do this, I plan to run a small semi-structured interview study with a mix of users recruited from Mastodon and outside Mastodon.
Rules and Content Moderation in the Fediverse
Work forthcoming
Background
Rules and norms play an essential role in the operation of online communities.1
Commercial social web sites like Reddit have site-wide rules which apply to all communities,2 but decentralized online social networks like Mastodon do not have these.3
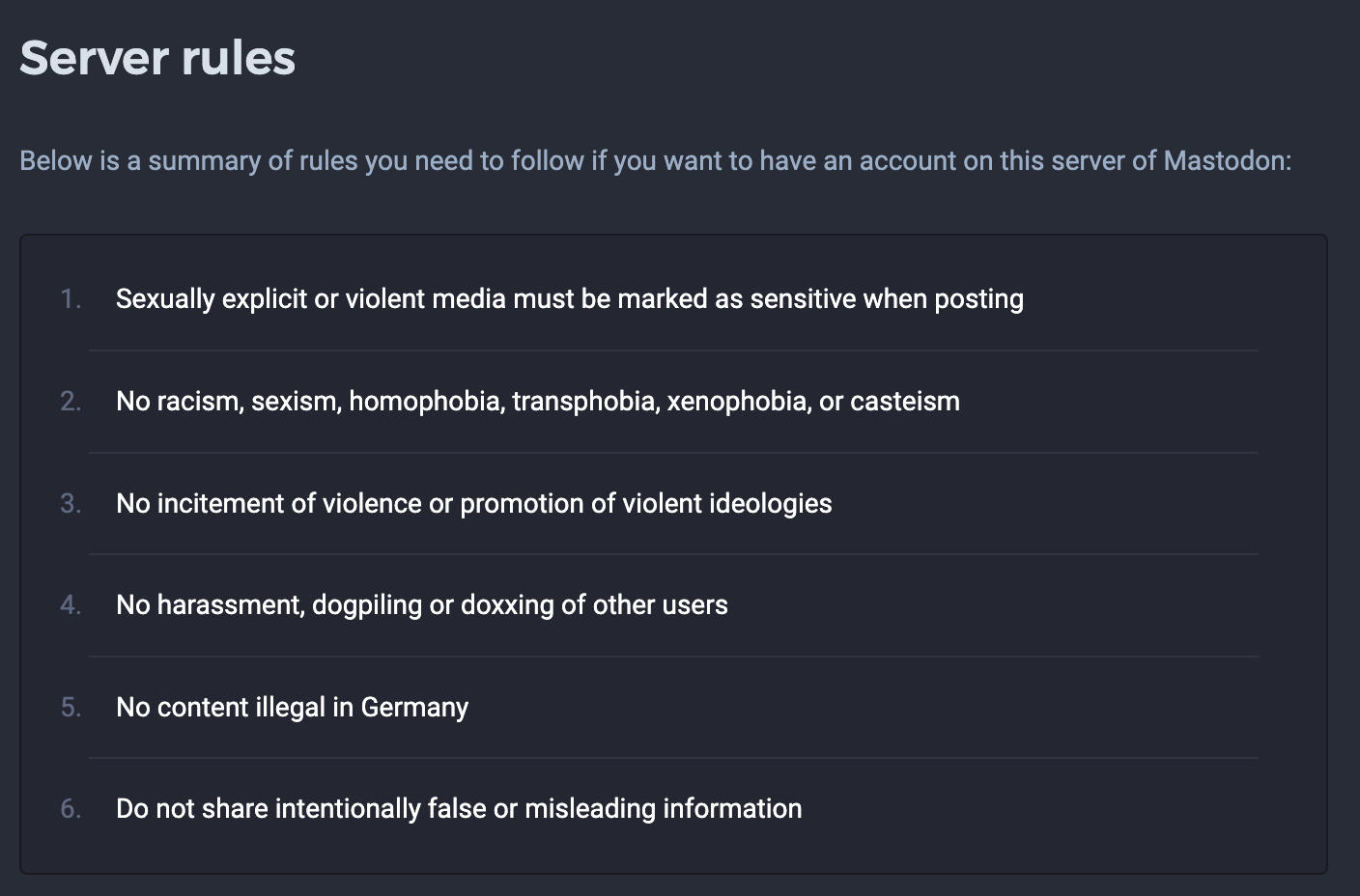
Mastodon servers tend to adopt the same rules

Puzzle: the Fediverse promises autonomy and indepedence, but servers look very similar in practice.
RQ1: How do rules originate and spread on the Fediverse?
RQ2: Why do Fediverse servers have similar rules?
Data
| ID | Software | Size | Topic |
|---|---|---|---|
| FV1 | Mastodon | [100–1K) | Regional |
| FV2 | Mastodon | [1K–10K) | Language |
| FV3 | Mastodon | [10–100) | Interest/Language |
| FV4 | Mastodon | [1K–10K) | Interest(?) |
| FV5 | Mastodon | [10-100) | Regional/Interst |
| FV6 | Pleroma | ||
| FV7 | Mastodon | [100–1K) | |
| FV8 | Mastodon | [100–1K) | |
| FV9 | Mastodon | [1K–10K) | |
| FV10 | Mastodon | [100–1K) | |
| FV11 | Mastodon | [100–1K) | |
| FV12 | Mastodon | [10–100) | |
| FV13 | Mastodon | [100–1K) | Interest |
| FV14 | Pleroma | ||
| FV15 | Pleroma | Religion | |
| FV16 | Misskey | ||
| FV17 | Mastodon | [100–1K) |
Quantitative data processing
Most common rules
| Rule | Count |
|---|---|
| No racism, sexism, homophobia, transphobia, xenophobia, or casteism | 1925 |
| No incitement of violence or promotion of violent ideologies | 1629 |
| No harassment, dogpiling or doxxing of other users | 1581 |
| No illegal content. | 1273 |
| Sexually explicit or violent media must be marked as sensitive when posting | 1220 |
| Do not share intentionally false or misleading information | 1074 |
| Be nice. | 510 |
| No spam or advertising. | 410 |
| Don't be a dick. | 405 |
| Be excellent to each other. | 264 |
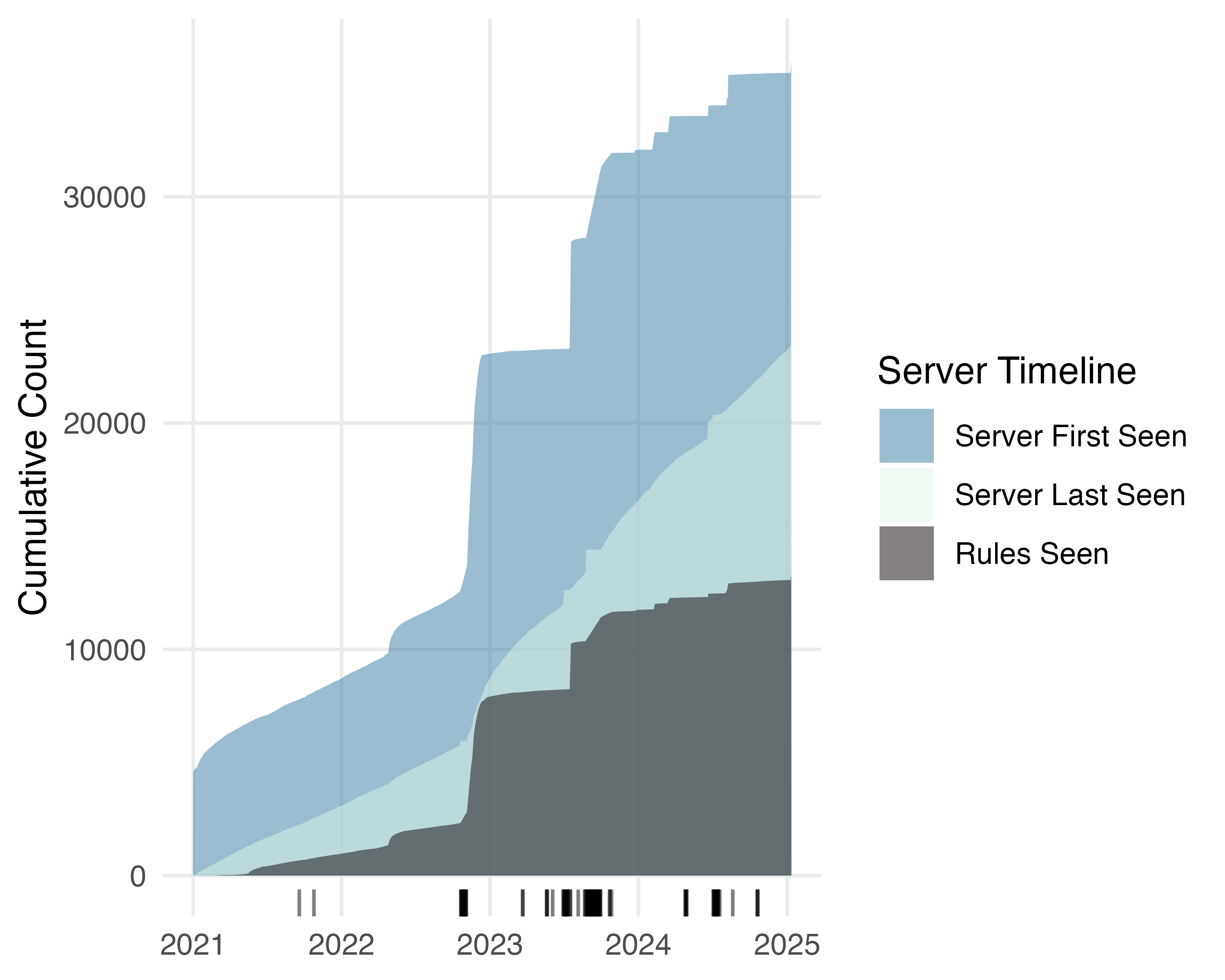
Questions I still intend to answer with the longitudinal data
How many Mastodon servers have rules?
What predicts if a server has rules?
How often do rules change? (Not very often)
Do similar servers adopt similar rules? (e.g. can we predict rule adoption)
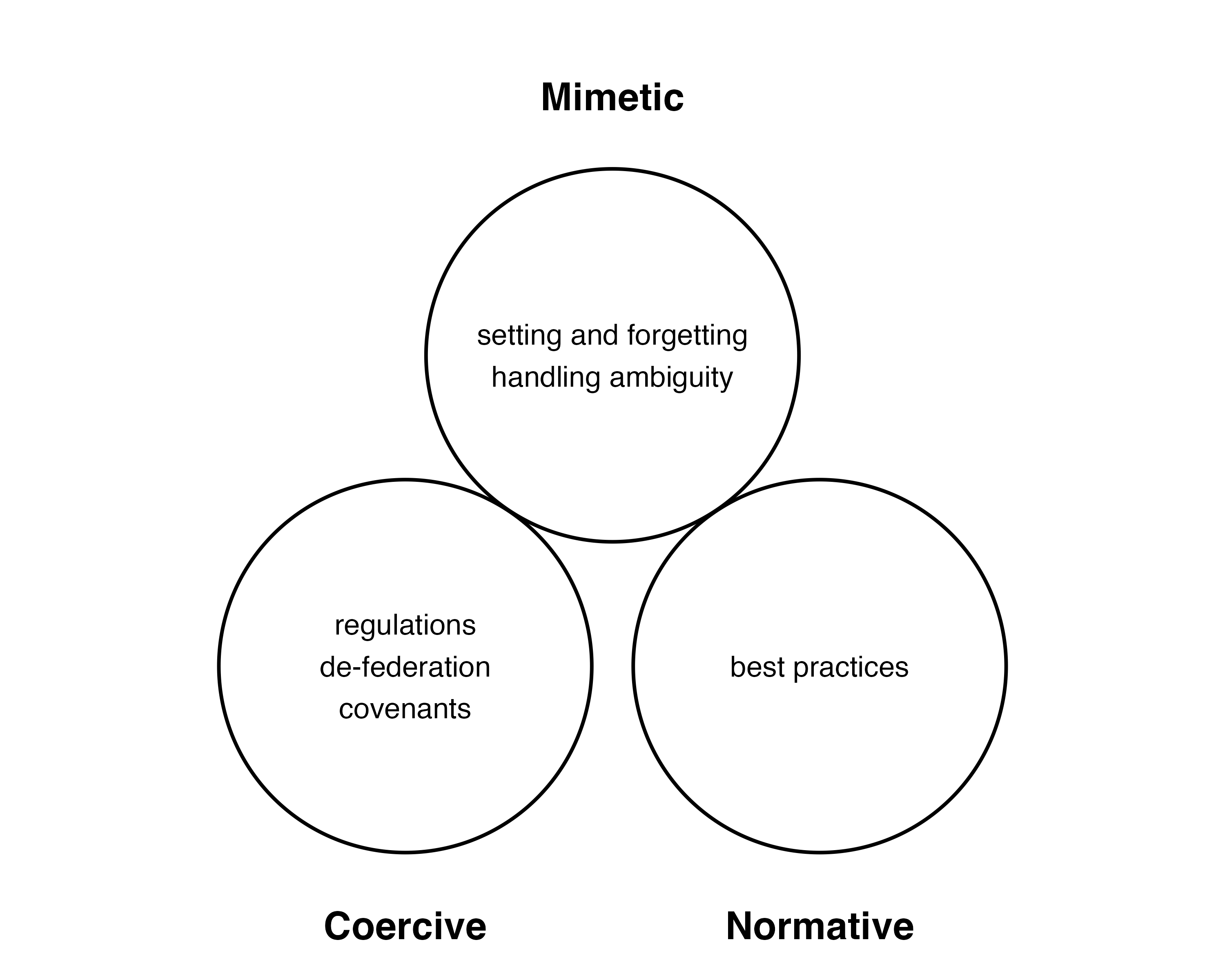
Initial Findings
Mastodon rules are created in a process consistent with instutional isomorphism.1
Qualitative Findings
Applying local rules to external posts
Proactive vs. reactive moderation
Rules as signposts
Rules to solicit reports
Network integrity



Social Interoperability
While ActivityPub allowed the fledgling Fediverse to interconnect, as a sociotechnical system, much of the social infrastructure is still developing.
Trust & Safety: Organizations like Independent Federated Trust & Safety (IFTAS) and the Social Web Foundation help admins coordinate and grow the ecosystem.
Reliability: Agreements like the Mastodon Server Covenant ensure servers will give people notice before shutting down and have at least one person availible in case of emergencies.1
Best Practices: Emerging research suggests challenges for admins and how to best deal with them.2